Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was one of the most remarkable civilizations in history, flourishing along the Nile River in northeastern Africa for over three millennia. It began around 3100 BC with the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh, Menes (also known as Narmer), and lasted until the conquest by Alexander the Great in 332 BC.
Key Points about Ancient Egypt:
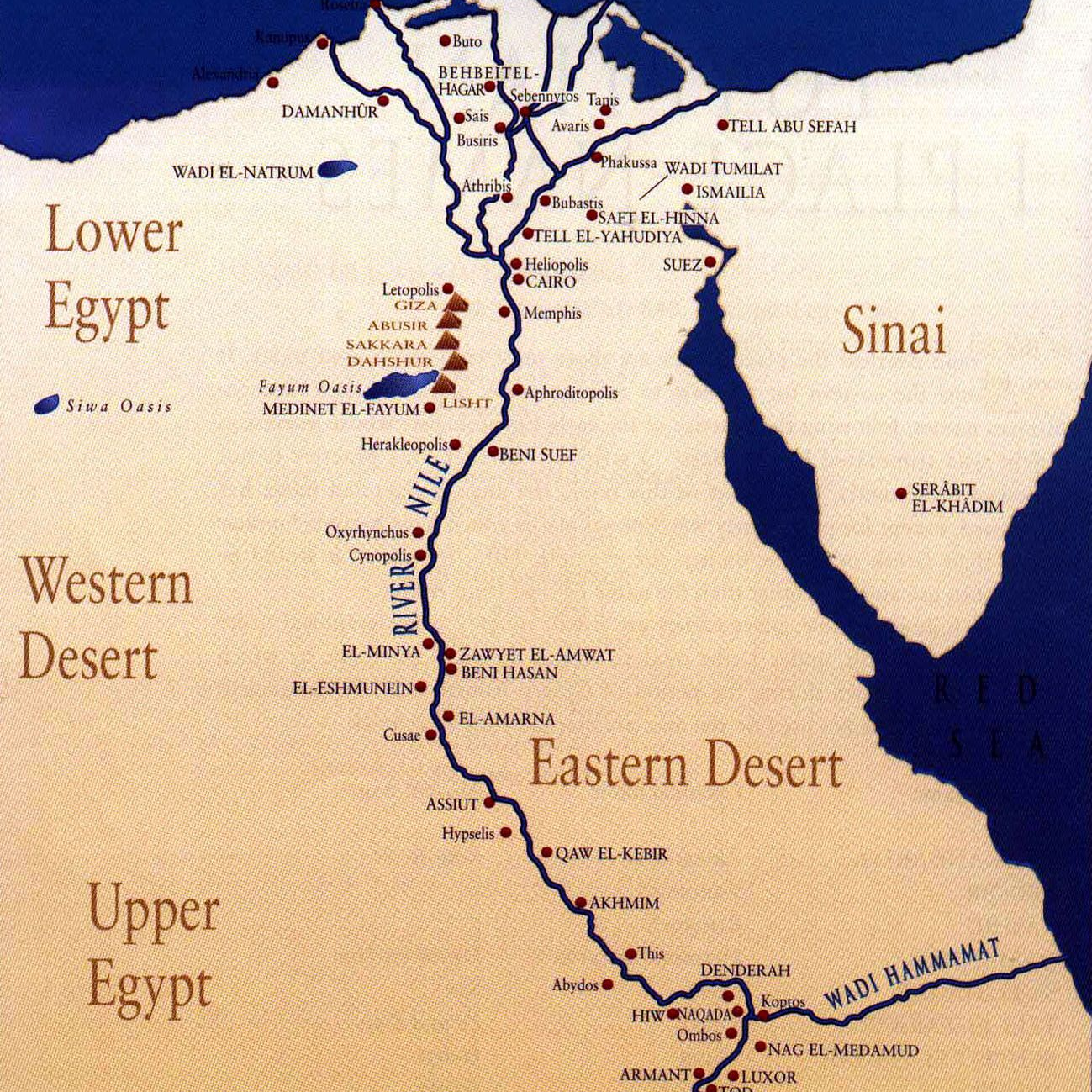
Geography: Ancient Egypt was centered around the Nile River, which provided fertile land for agriculture. The predictable flooding of the Nile allowed for the cultivation of crops, supporting a dense population and the development of a complex society.

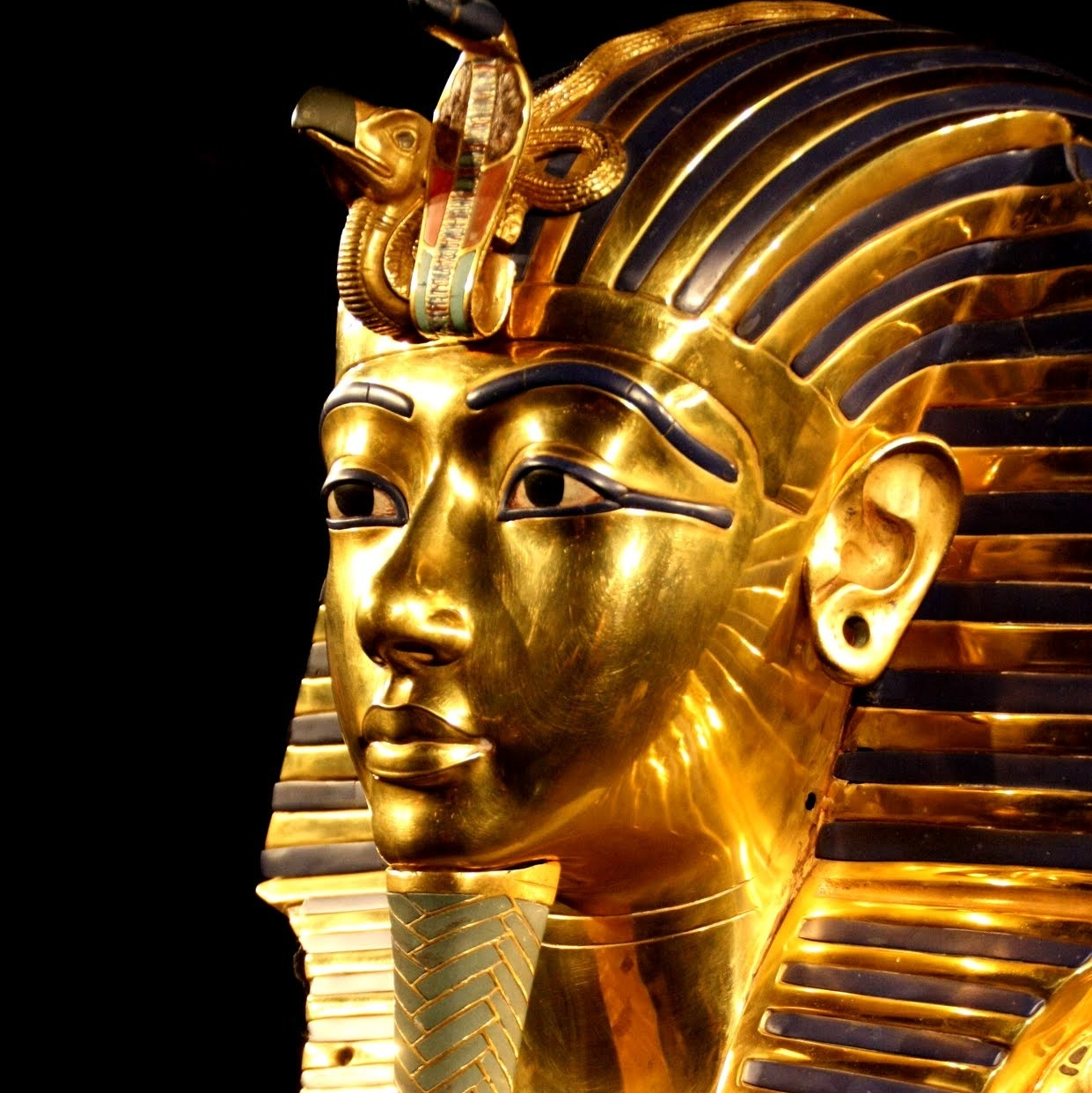
Pharaohs: The rulers of Egypt, known as pharaohs, were considered divine and held absolute power. Some of the most famous pharaohs include Tutankhamun, Ramses II, and Cleopatra VII.

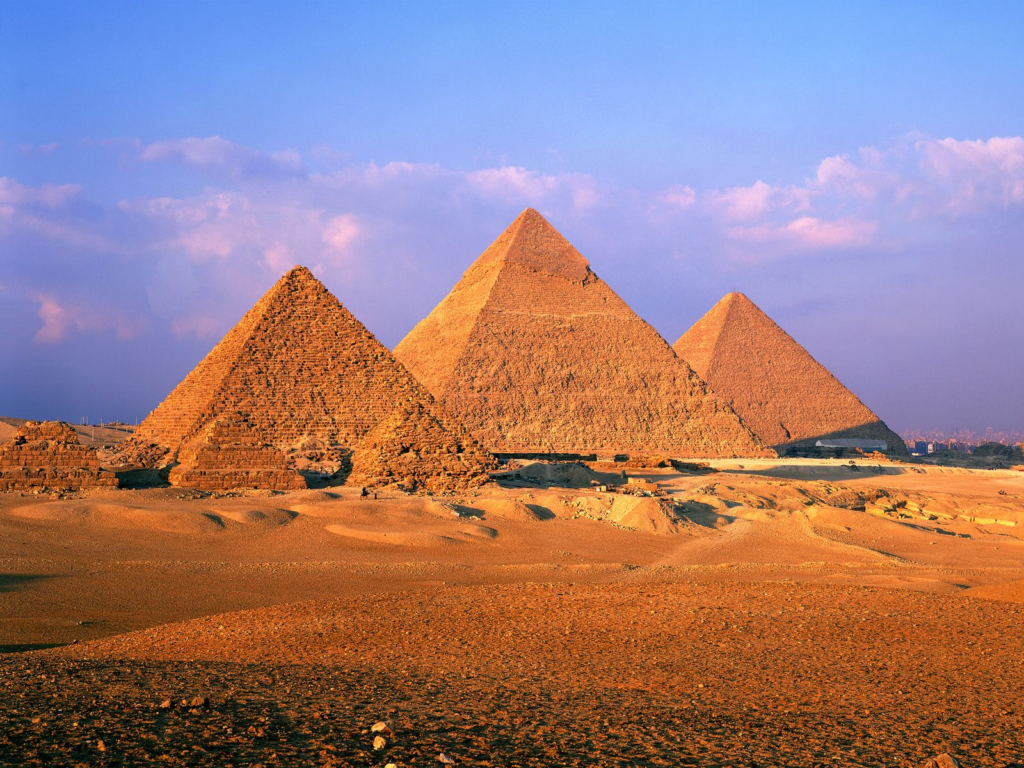
Pyramids: The Egyptians are renowned for their monumental architecture, especially the pyramids. The Great Pyramid of Giza, built for Pharaoh Khufu, is one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.

Religion: Religion played a central role in Egyptian life. They believed in a pantheon of gods and goddesses, such as Ra (the sun god), Osiris (the god of the afterlife), and Isis (the goddess of magic and motherhood). The afterlife was a significant aspect of their belief system, leading to elaborate burial practices and the construction of tombs.
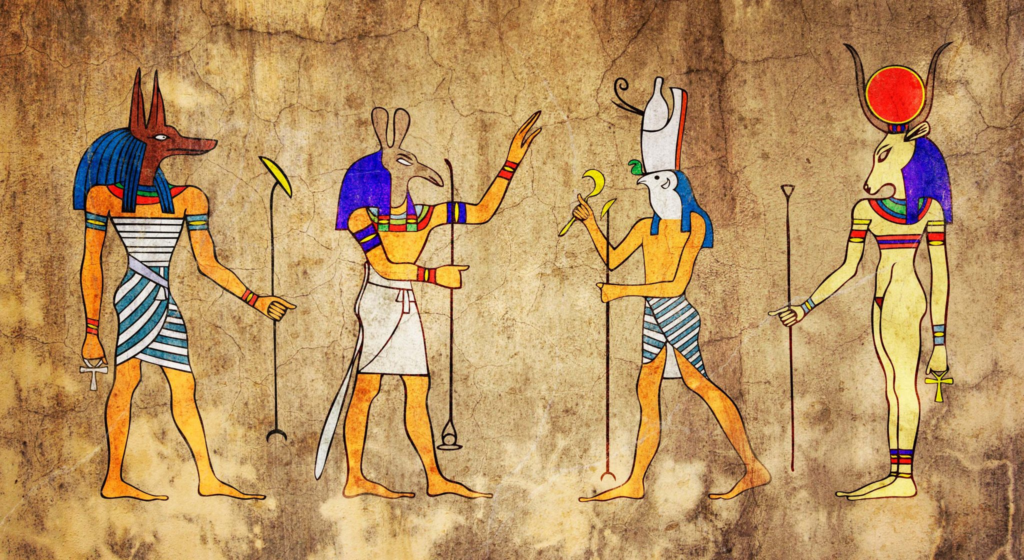
Writing: The Egyptians developed one of the earliest writing systems, known as hieroglyphics. This script was used for religious texts, official inscriptions, and monumental art.

Achievements: Ancient Egypt made significant advancements in various fields, including medicine, mathematics, and engineering. They also excelled in art, producing intricate jewelry, pottery, and sculptures.

Society and Daily Life:

- Social Structure: Ancient Egyptian society was highly stratified. At the top were the pharaoh and the royal family, followed by priests and nobles, scribes, artisans, and farmers. At the bottom were slaves and laborers.
- Housing: Most Egyptians lived in mudbrick houses. Wealthier families had larger homes with multiple rooms, while poorer families lived in simple, one-room structures.
- Clothing: Egyptians wore simple linen garments. Men typically wore kilts, while women wore dresses. Both men and women adorned themselves with jewelry and cosmetics.
- Food: The diet was largely based on bread and beer, supplemented by vegetables, fruits, fish, and meat. The fertile Nile Delta provided an abundance of food resources.
- Entertainment: Music, dance, and board games were popular forms of entertainment. Senet, an ancient board game, was especially favored by Egyptians.
Education and Learning:
- Education: Education was primarily reserved for the elite. Boys from wealthy families were trained as scribes, learning to read and write hieroglyphics. Girls were generally educated at home in domestic skills.
- Libraries and Learning Centers: Temples often served as centers of learning, housing extensive collections of scrolls and serving as training grounds for priests and scholars.
Economy and Trade:
- Agriculture: The economy was heavily reliant on agriculture. The annual flooding of the Nile deposited rich silt on the land, making it highly fertile for growing crops such as wheat, barley, and flax.
- Trade: Egypt engaged in extensive trade with neighboring regions. They traded gold, papyrus, linen, and grain for goods such as cedar wood from Lebanon, incense from Punt, and lapis lazuli from Afghanistan.
Architecture and Engineering:
- Pyramids and Tombs: The construction of pyramids and tombs required advanced engineering skills. The pyramids served as burial sites for pharaohs and were believed to help them in their journey to the afterlife.
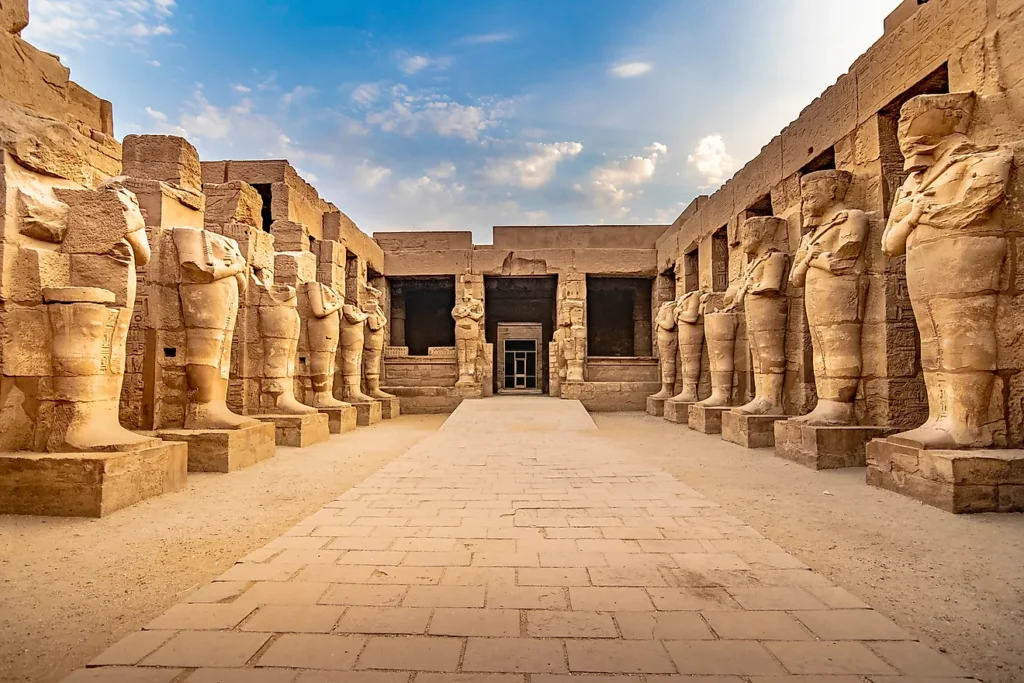
- Temples: Temples were built to honor the gods and goddesses. Notable temples include the Karnak Temple complex and the Temple of Luxor.
- Monuments: Obelisks, tall and slender monuments, were erected to commemorate significant events or honor deities.
Scientific Achievements:

- Medicine: Ancient Egyptians practiced an advanced form of medicine, performing surgeries and using a variety of herbal remedies. They also had knowledge of anatomy, as evidenced by their mummification practices.
- Mathematics: They developed a system of mathematics that included geometry, necessary for constructing their architectural marvels.
- Astronomy: Egyptians had a keen interest in astronomy, using the stars to develop their calendar and align their pyramids.


I am extremely inspired along with your writing skills and
also with the layout for your weblog. Is that this a paid theme or
did you modify it yourself? Anyway stay up the nice high quality writing, it
is rare to see a nice weblog like this one these days. TikTok Algorithm!